View the last(seventh) part of this post : What is the motive or the theory behind Performance Appraisal? VII (New Method of Goal Achievement)
BEHAVIORALLY ANCHORED RATING SCALES
Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) is a relatively new technique which combines the graphic rating scale and critical incidents method. It consists of predetermined critical areas of job performance or sets of behavioural statements describing important job performance qualities as good or bad (for eg. the qualities like inter personal relationships, adaptability and reliability, job knowledge etc). These statements are developed from critical incidents.
In this method, an employee’s actual job behaviour is judged against the desired behaviour by recording and comparing the behaviour with BARS. Developing and practicing BARS requires expert knowledge.
HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING METHOD
Human resources are valuable assets for every organization. Human resource accounting method tries to find the relative worth of these assets in the terms of money. In this method the Performance appraisal of the employees is judged in terms of cost and contribution of the employees. The cost of employees include all the expenses incurred on them like their compensation, recruitment and selection costs, induction and training costs etc whereas their contribution includes the total value added (in monetary terms). The difference between the cost and the contribution will be the performance of the employees. Ideally, the contribution of the employees should be greater than the cost incurred on them.
Now we are done with the Goal Setting Exercise quite elaborately. I invite your comments on how you can benefit from these informations in your professional and personal life.
However, now we will move ahead to the next step in the Performance Appraisal System i.e. Performance Assessment or Performance Evaluation.
Before going ahead with my discussion on this process elaborately, I would like to introduce you all to the different tools of Performance Appraisal that have been categorized according to the Assessment Method.
First of all we will discuss the Traditional Methods in practice. They can be named and described as following:-
1. ESSAY APPRAISAL METHOD This traditional form of appraisal, also known as "Free Form method" involves a description of the performance of an employee by his superior. The description is an evaluation of the performance of any individual based on the facts and often includes examples and evidences to support the information. A major drawback of the method is the inseparability of the bias of the evaluator.
2. STRAIGHT RANKING METHOD This is one of the oldest and simplest techniques of performance appraisal. In this method, the appraiser ranks the employees from the best to the poorest on the basis of their overall performance. It is quite useful for a comparative evaluation.
2. STRAIGHT RANKING METHOD This is one of the oldest and simplest techniques of performance appraisal. In this method, the appraiser ranks the employees from the best to the poorest on the basis of their overall performance. It is quite useful for a comparative evaluation.
3. PAIRED COMPARISON A better technique of comparison than the straight ranking method, this method compares each employee with all others in the group, one at a time. After all the comparisons on the basis of the overall comparisons, the employees are given the final rankings.
4. CRITICAL INCIDENTS METHODS In this method of Performance appraisal, the evaluator rates the employee on the basis of critical events and how the employee behaved during those incidents. It includes both negative and positive points. The drawback of this method is that the supervisor has to note down the critical incidents and the employee behaviour as and when they occur.
5. FIELD REVIEW In this method, a senior member of the HR department or a training officer discusses and interviews the supervisors to evaluate and rate their respective subordinates. A major drawback of this method is that it is a very time consuming method. But this method helps to reduce the superiors’ personal bias.
6. CHECKLIST METHOD The rater is given a checklist of the descriptions of the behaviour of the employees on job. The checklist contains a list of statements on the basis of which the rater describes the on the job performance of the employees.
7. GRAPHIC RATING SCALE In this method, an employee’s quality and quantity of work is assessed in a graphic scale indicating different degrees of a particular trait. The factors taken into consideration include both the personal characteristics and characteristics related to the on the job performance of the employees. For example a trait like Job Knowledge may be judged on the range of average, above average, outstanding or unsatisfactory.
8. FORCED DISTRIBUTION To eliminate the element of bias from the rater’s ratings, the evaluator is asked to distribute the employees in some fixed categories of ratings like on a normal distribution curve. The rater chooses the appropriate fit for the categories on his own discretion.
4. CRITICAL INCIDENTS METHODS In this method of Performance appraisal, the evaluator rates the employee on the basis of critical events and how the employee behaved during those incidents. It includes both negative and positive points. The drawback of this method is that the supervisor has to note down the critical incidents and the employee behaviour as and when they occur.
5. FIELD REVIEW In this method, a senior member of the HR department or a training officer discusses and interviews the supervisors to evaluate and rate their respective subordinates. A major drawback of this method is that it is a very time consuming method. But this method helps to reduce the superiors’ personal bias.
6. CHECKLIST METHOD The rater is given a checklist of the descriptions of the behaviour of the employees on job. The checklist contains a list of statements on the basis of which the rater describes the on the job performance of the employees.
7. GRAPHIC RATING SCALE In this method, an employee’s quality and quantity of work is assessed in a graphic scale indicating different degrees of a particular trait. The factors taken into consideration include both the personal characteristics and characteristics related to the on the job performance of the employees. For example a trait like Job Knowledge may be judged on the range of average, above average, outstanding or unsatisfactory.
8. FORCED DISTRIBUTION To eliminate the element of bias from the rater’s ratings, the evaluator is asked to distribute the employees in some fixed categories of ratings like on a normal distribution curve. The rater chooses the appropriate fit for the categories on his own discretion.
15% high performance
20% High average performance
30% average performance
20% low average performance
15% low performance
Now listed out below are the Modern Methods. They can be named and described as follows:-
ASSESSMENT CENTRES -
An assessment centre typically involves the use of methods like social/informal events, tests and exercises, assignments being given to a group of employees to assess their competencies to take higher responsibilities in the future. Generally, employees are given an assignment similar to the job they would be expected to perform if promoted. The trained evaluators observe and evaluate employees as they perform the assigned jobs and are evaluated on job related characteristics.
The major competencies that are judged in assessment centres are interpersonal skills, intellectual capability, planning and organizing capabilities, motivation, career orientation etc. assessment centres are also an effective way to determine the training and development needs of the targeted employees.
The major competencies that are judged in assessment centres are interpersonal skills, intellectual capability, planning and organizing capabilities, motivation, career orientation etc. assessment centres are also an effective way to determine the training and development needs of the targeted employees.
| |
BEHAVIORALLY ANCHORED RATING SCALES
Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) is a relatively new technique which combines the graphic rating scale and critical incidents method. It consists of predetermined critical areas of job performance or sets of behavioural statements describing important job performance qualities as good or bad (for eg. the qualities like inter personal relationships, adaptability and reliability, job knowledge etc). These statements are developed from critical incidents.
In this method, an employee’s actual job behaviour is judged against the desired behaviour by recording and comparing the behaviour with BARS. Developing and practicing BARS requires expert knowledge.
HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING METHOD
Human resources are valuable assets for every organization. Human resource accounting method tries to find the relative worth of these assets in the terms of money. In this method the Performance appraisal of the employees is judged in terms of cost and contribution of the employees. The cost of employees include all the expenses incurred on them like their compensation, recruitment and selection costs, induction and training costs etc whereas their contribution includes the total value added (in monetary terms). The difference between the cost and the contribution will be the performance of the employees. Ideally, the contribution of the employees should be greater than the cost incurred on them.
MANAGEMENT BY OBJECTIVE METHOD
The concept of ‘Management by Objectives’ (MBO) was first given by Peter Drucker in 1954. It can be defined as a process whereby the employees and the superiors come together to identify common goals, the employees set their goals to be achieved, the standards to be taken as the criteria for measurement of their performance and contribution and deciding the course of action to be followed.
The essence of MBO is participative goal setting, choosing course of actions and decision making. An important part of the MBO is the measurement and the comparison of the employee’s actual performance with the standards set. Ideally, when employees themselves have been involved with the goal setting and the choosing the course of action to be followed by them, they are more likely to fulfil their responsibilities.
THE MBO PROCESS
UNIQUE FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES OF MBO
The principle behind Management by Objectives (MBO) is to create empowered employees who have clarity of the roles and responsibilities expected from them, understand their objectives to be achieved and thus help in the achievement of organizational as well as personal goals.
Some of the important features and advantages of MBO are:
Some of the important features and advantages of MBO are:
- Clarity of goals – With MBO, came the concept of SMART goals i.e. goals that are:
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Realistic, and
Time bound.
The goals thus set are clear, motivating and there is a linkage between organizational goals and performance targets of the employees.
- The focus is on future rather than on past. Goals and standards are set for the performance for the future with periodic reviews and feedback.
- Motivation – Involving employees in the whole process of goal setting and increasing employee empowerment increases employee job satisfaction and commitment.
- Better communication and Coordination – Frequent reviews and interactions between superiors and subordinates helps to maintain harmonious relationships within the enterprise and also solve many problems faced during the period.
360 DEGREE FEEDBACK
360 degree feedback, also known as 'multi-rater feedback', is the most comprehensive appraisal where the feedback about the employees’ performance comes from all the sources that come in contact with the employee on his job.
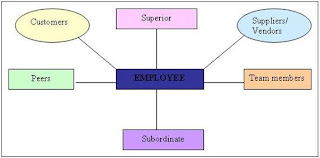
360 degree respondents for an employee can be his/her peers, managers (i.e. superior), subordinates, team members, customers, suppliers/ vendors - anyone who comes into contact with the employee and can provide valuable insights and information or feedback regarding the "on-the-job" performance of the employee.
360 degree appraisal has four integral components:
1. Self appraisal
2. Superior’s appraisal
3. Subordinate’s appraisal
4. Peer appraisal.
Self appraisal gives a chance to the employee to look at his/her strengths and weaknesses, his achievements, and judge his own performance. Superior’s appraisal forms the traditional part of the 360 degree performance appraisal where the employees’ responsibilities and actual performance is rated by the superior.
Subordinates appraisal gives a chance to judge the employee on the parameters like communication and motivating abilities, superior’s ability to delegate the work, leadership qualities etc. Also known as internal customers, the correct feedback given by peers can help to find employees’ abilities to work in a team, co-operation and sensitivity towards others.
Self assessment is an indispensable part of 360 degree appraisals and therefore 360 degree Performance appraisal have high employee involvement and also have the strongest impact on behavior and performance. It provides a "360-degree review" of the employees’ performance and is considered to be one of the most credible performance appraisal methods.
360 degree performance appraisal is also a powerful developmental tool because when conducted at regular intervals (say yearly) it helps to keep a track of the changes others’ perceptions about the employees. A 360 degree appraisal is generally found more suitable for the managers as it helps to assess their leadership and managing styles. This technique is being effectively used across the globe for performance appraisals. Some of the organizations following it are Wipro, Infosys, and Reliance Industries etc.
1. Self appraisal
2. Superior’s appraisal
3. Subordinate’s appraisal
4. Peer appraisal.
Self appraisal gives a chance to the employee to look at his/her strengths and weaknesses, his achievements, and judge his own performance. Superior’s appraisal forms the traditional part of the 360 degree performance appraisal where the employees’ responsibilities and actual performance is rated by the superior.
Subordinates appraisal gives a chance to judge the employee on the parameters like communication and motivating abilities, superior’s ability to delegate the work, leadership qualities etc. Also known as internal customers, the correct feedback given by peers can help to find employees’ abilities to work in a team, co-operation and sensitivity towards others.
Self assessment is an indispensable part of 360 degree appraisals and therefore 360 degree Performance appraisal have high employee involvement and also have the strongest impact on behavior and performance. It provides a "360-degree review" of the employees’ performance and is considered to be one of the most credible performance appraisal methods.
360 degree performance appraisal is also a powerful developmental tool because when conducted at regular intervals (say yearly) it helps to keep a track of the changes others’ perceptions about the employees. A 360 degree appraisal is generally found more suitable for the managers as it helps to assess their leadership and managing styles. This technique is being effectively used across the globe for performance appraisals. Some of the organizations following it are Wipro, Infosys, and Reliance Industries etc.
Arguments Against 360 Degree Performance Appraisal
Despite the fact that 360 degree appraisals are being widely used throughout the world for appraising the performance of the employees at all levels, many HR experts and professionals argument against using the technique of 360 degree appraisals. The main arguments are:
- 360 performance rating system is not a validated or corroborated technique for Performance appraisal.
- With the increase in the number of raters from one to five (commonly), it become difficult to separate, calculate and eliminate personal biasness and differences.
- It is often time consuming and difficult to analyze the information gathered.
- The results can be manipulated by the employees towards their desired ratings with the help of the raters.
- The 360 degree appraisal mechanism can have a adversely effect the motivation and the performance of the employees.
- 360 degree feedback – as a process requires commitment of top management and the HR, resources(time, financial resources etc), planned implementation and follow up.
- 360 degree feedback can be adversely affected by the customers perception of the organisation and their incomplete knowledge about the process and the clarity of the process.
- Often, the process suffers because of the lack of knowledge on the part of the participants or the raters.
After going through all these methods you must have got the idea as to which one of the method we are following and which is the best optimum method to follow.
Actually speaking no method is full proof in itself and all have its advantages and disadvantages but the cache here is that why not study, review and pick the best from each method and come up with our own method which suits us and our organizational setup and above all the stars in this process the EMPLOYEES.
So in the next post we will thoroughly discuss the Performance Review or Assessment as it goes.